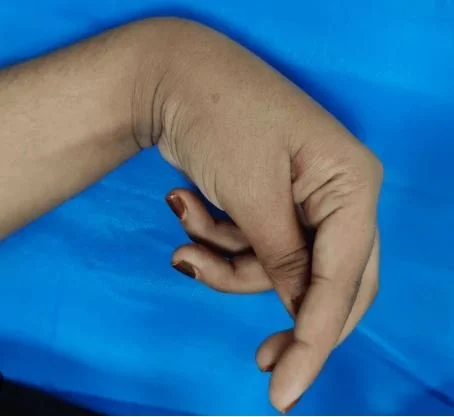
A 39 y.o. violinist comes in with an abnormality of the hand. It prevents him from playing.
What is it?
spasm of the hand
Our patient had hand dystonia.
Dystonia is a disabling disorder of motor control resulting in involuntary muscle contractions. It is classified by age of onset with those occurring before age 27 considered childhood-onset. Adult- onset dystonias begin later and most occur in the upper half of the body as in our patient. Dystonias are centrally mediated but other conditions can cause muscle activity triggered by peripheral nerves.
Examples of centrally mediated dystonia include:
1. Writer’s cramp is a well-known example. The mean age of onset is 38 and it manifests as an extremely tight grip with excessive finger and wrist flexion. This makes writing very difficult. Task specific dystonias of the upper extremity must be differentiated from overuse syndromes like median or ulnar nerve entrapments.
2. Musician’s cramp refers to a dystonia during a musical performance that causes abnormal posturing and inability to perform. This can be devastating to a performer and lead to a change in careers for professional musicians.
3. Dystonias can develop with acute or chronic exposure to antidopaminergic drugs such as prochlorperazine or neuroleptics.
These central dystonias are thought to originate in the basal ganglia and are common in diseases like Parkinson’s or Wilson’s disease where infiltration of the basal ganglia occurs. Deep brain stimulation is offered as a possible treatment. In cases of focal dystonia, like laryngeal dystonia, local injections of botulinum toxin can be useful.
Robert Kennedy has laryngeal dystonia
Neuromuscular hyperexcitability can also be triggered by peripheral nerves. Tetany is the term to describe this neuromuscular phenomenon.
Peripheral excitability of nerves can cause muscle contraction leading to carpopedal spasm. Hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, and alkalosis can lead to these spasms involving the skeletal muscles as well as the larynx.
carpopedal spasm is a dystonia caused by compazine
Dystonia can also result from a combination of central and peripheral nerve stimulation as in tetanus. A bacterial toxin, tetanospasmin, Is produced in a wound and travels to the spinal cord and brainstem where it blocks the release of GABA (a muscle relaxant) leading to uncontrolled excitation of motor neurons. As a result, the jaw locks and there is marked arching of the back. Tetanus acts peripherally and causes local paralysis of muscles immediately surrounding the wound site.
Infantile tetanus can present with marked spasm of the back resulting in episthotonus.
Unfortunately, our patient did not respond to anticholinergics, muscle relaxants, or antiseizure drugs. He was being considered for deep brain stimulation.
Torres-Russotto D, Perlmutter J. Focal dystonias of the hand and upper extremity. J Hand Surg Am. 2008 Nov;33(0):1657-1658.
Weiss EM, Hershey T, Karimi M, Racette B, Tabbal SD, Mink JW, et al. Relative risk of spread of symptoms among the focal onset primary dystonias. Mov Disord. 2006;21:1175–1181.
Hammami H, Jeddi C, Kilani M. Acute drug-induced dystonia: emergency department presentation and management. Toxicologie analytique et Clinique.
Neychev V, Gross R, Lehericy S, et al. The functional neuroanatomy of dystonia. Neurobiol Dis. 2011 Feb;42(2):185-201