A 58 y.o. male sp ablation for a fib x 2 comes to the ED with L arm and L leg weakness
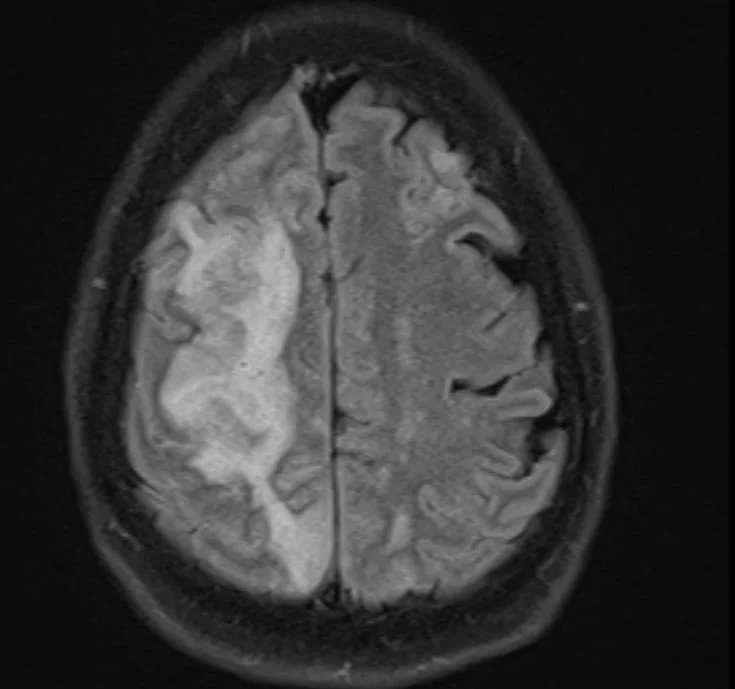
His MRI is shown below
what is the differential for the kind of stroke he suffered?
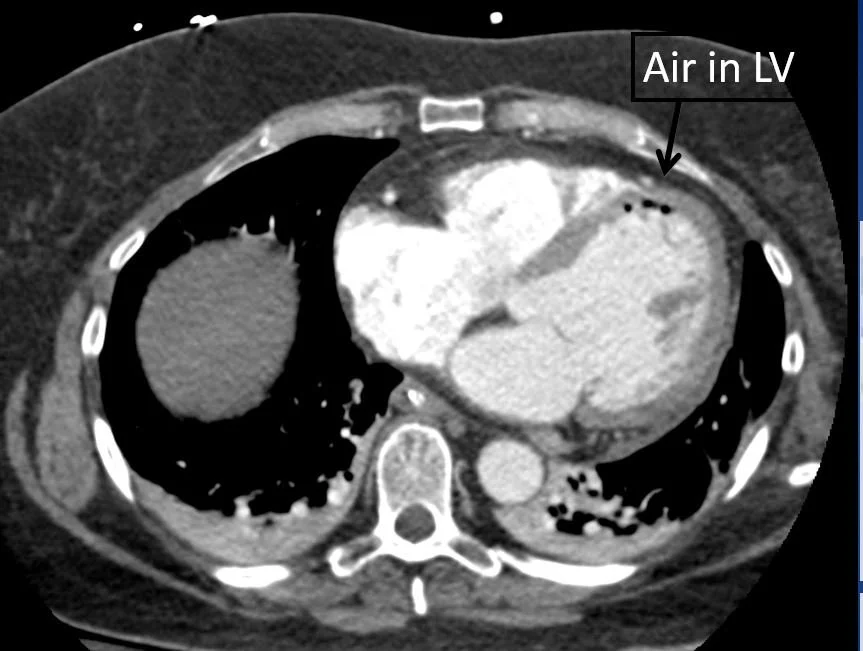
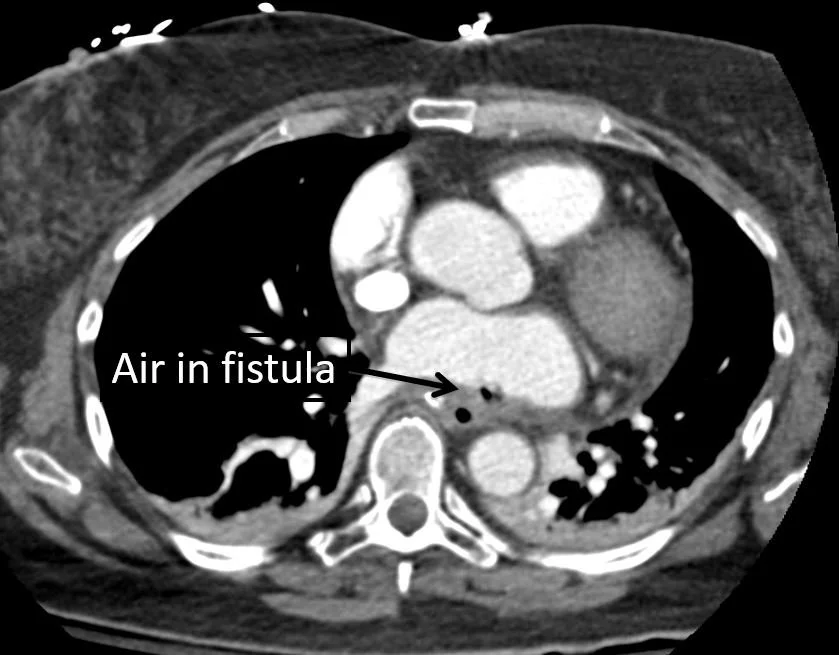
Our patient had an atrio -esophageal fistula after his ablation and suffered an air embolus causing a stroke.
Air was seen in the LV
air was seen in the fistula
Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects 9% of adults over the age of 80. Non-valvular AF is associated with a 3 to 5-fold increase in stroke risk and therefore anticoagulation is recommended. However, anticoagulation itself poses risks since between 2 and 7% of patients will have major bleeding. Many older individuals are fall risks and in DOAC (direct oral anticoagulant) trials up to 0.9% had significant head bleeds. Because of significant risks; ablation and L atrial appendage closures are being performed.
ABLATION
The cornerstone of atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation is radiofrequency ablation of the area around the pulmonary veins. This is done using radio waves to heat and destroy nerve tissue. In many patients with persistent AF this requires higher frequency for the ablation. This causes inflammation and can lead to complications like fistulae.
In the case of our patient an air embolus occurred through an atrio-esophageal fistula. Other complications can occur as well: massive GI bleeding, pulmonary vein occlusion, and sepsis. It is recommended that an esophageal temperature probe be used as well an also occur as power reduction.
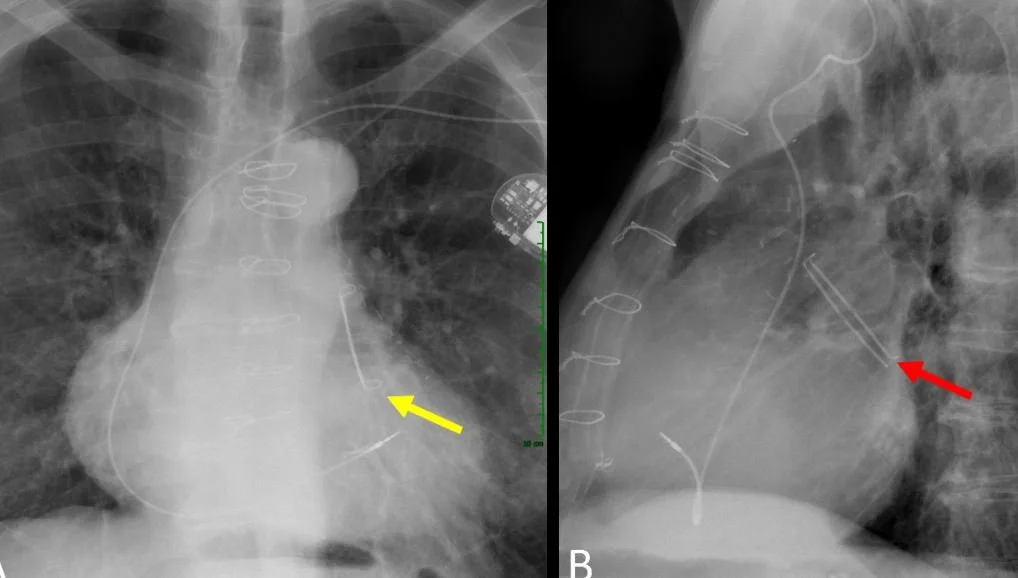
all that can be seen on cxr is the central knob of the WATCHMAN
during placement the intra atrial septum must be punctured to place the device.
LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE CLOSURE
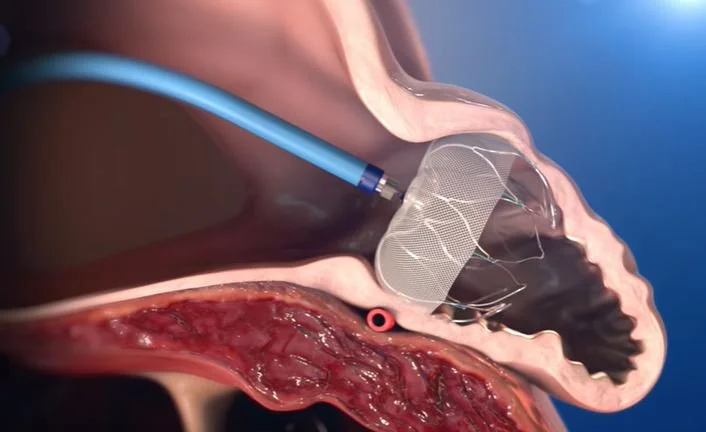
Currently another procedure can be offered; occlusion of the L atrial appendage. This is where most clots form and by occluding the opening they cannot escape into the aorta to cause stroke. The procedure is called WATCHMAN or amulet and can be done through the femoral vein . After implantation a TEE is performed to confirm placement and closure of the left atrial appendage.
In the PROTECT AF trial there was a high risk of procedure related complications with the WATCHMAN including pericardial tamponade, major bleeding , stroke , and device embolization. These usually occur in the first 24 hours. The OPTION 2025 trial found the newer generation WATCHMAN device to be non-inferior when compared to AF ablation and anticoagulation.
Our patient had an esophageal stent placed and was sent to rehab for his stroke.
the L atrial appendage can also be closed with a clip.
Pappone C, Vicedomini G, Santinelli V. Atrio-esophageal fistula after AF ablation: pathophysiology, prevention and treatment. J Atr Fibrillation 2013 Oct 31;6(3):860.
Perotta L, Bordignon A, Dugo D. Complications from left atrial appendage exclusion devices. J Atr Fibrillation 2014 Jun 307(1):1034.
Kaafarani M, Saw J, Daniels M, et al. Rose of CT imaging in left atrial appendage occlusion for the WATCHMAN device. Cardiovac Diagn Ther. 2020 Feb;10(1):45-58.
Kocian M, Kosowski M, Mazurkiewicz M, et al. Bleeding complications of anticoagulation therapy in clinical practice—epidemiology and management: review of the literature. Biomedicines 2024 Oct 1;12(10):2242.
Wazni O, Saliba W, Nair D. Left atrial appendage closure after ablation for atrial fibrillation. NEJM 2025;392:1277-1287.