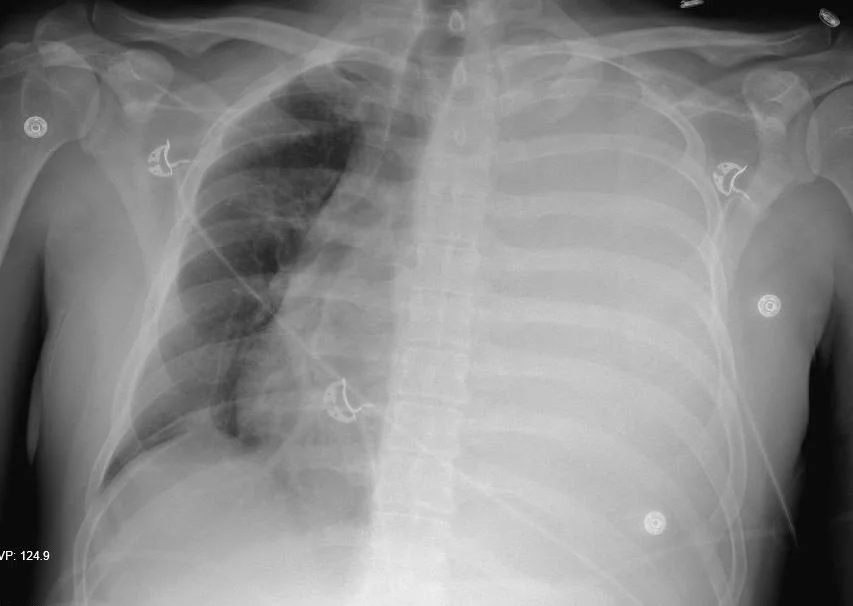
A 33 y.o. male presents with shortness of breath and stable vitals
What is the first thing you want to do?
The first thing to do is take a history. Our patient had an squamous cell variant tumor called a NUT tumor and thrombocytopenia. This tumor is rare and is defined by rearrangements of the NUT gene on chromosome 15q14 where it fuses to another chromosome causing a chimera; usually 15 translocates to 19. The karyotypes often have only this single abnormality suggesting the effect of a fusion oncogene. This is similar to the Philadelphia chromosome in chronic myelogenous leukemia where there is a translocation of chromosome 9 and 22.
The NUT tumor does not arise from any specific organ but presents as a poorly differentiated carcinoma arising from midline locations such as the head, neck or mediastinum. The first person to have a NUT midline carcinoma was a 12 year old girl was described in 1999 who had a sore throat and muffled voice. She was found to have an aggressive tumor involving the epiglottis. The genetic material was sequenced and found to have an abnormality in chromosome 15. It was names NUT because it was originally found only in the testis ( hence NUclear protein in Testis). The name has since been changed to “chr15orf55”.
The tumors are now found to include 7% of carcinomas in patients less than 40 with the youngest patient reported at age 3. About 39% of the tumors arise in the head and neck.
NUT tumor of the L medial canthus. The ciliary ganglion is the only other place in the body where the NUT gene is normally found.
Since 80% of patients die within one year a multimodal approach with systemic chemotherapy, surgery and radiation is the current clinical practice. When the NUT gene merges with another gene it blocks epithelial squamous differentiation leading to a proliferation of immature neoplastic cells. These fused proteins are the target of current research.
CLINICAL PEARL
Death, perforation of the R and L ventricle, pericardial tamponade, and mediastinal perforation with R sided hemothorax have all been reported with L chest tube placement.
pseudoaneursym causing exsanguination after chest tube placement.
Our patient underwent a thoracentesis of 2 L of bloody fluid. His platelet count was 28,000 and he was given platelets and blood. A thal quick was placed which subsequently clotted and a chest tube was placed draiining an additional liter. Since each hemithorax can hold 40% of a patient’s blood volume, consideration was given to possible exsanguination from the chest tube and thoracic surgery was called. Our patient stabilized and was treated for sepsis. Imaging showed no active extravasation and widespread tumor with mets to bone and pleura. He was discharged home on hospice.
French C. NUT midline carcinoma. Cancer Genetics and Cytogenetics. 2010 Nov;20391):16-20.
Napolitano M, Venturelli M et al. NUT midline carcinoma of the head and neck: current perspectives. Onco Target Ther 2019;12:3235-3244.
Chau N, Ma C, Danga K, et al. A nevel prognostic risk classification model for NUT midline cardinoma: a largest cohort analysis from the NMC registry Clin Onco. 2018.36.15_suppl. 6085. Soi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.36.15_suppl. 6085