A 62 y.o. woman presents with chest pain after a roll over MVC
Why does she have chest pain?
Our pt had a hx of breast reduction surgery and after the accident had active arterial extravasation within her L breast. So, while restraints are useful, they can also be a source of injury since the point of contact of a seat belt holds that portion of the body in a fixed position while the rest of the body rotates around it. Seat belts were first introduced in 1894 and the lap belt became standard in 1964. In 1973 the three point restraint was introduced with airbags in the mid 1970’s.
Seat belts have two functions; to prevent ejection from the vehicle and to keep the head from hitting the windshield. It is estimated that seat belts reduce fatalities by 43%. Airbags on the other hand, were designed to provide a cushion between the driver and the steering wheel or dash in the event of a crash. Since there is a fixed point around which the body rotates with seat belts, compression of the bowel between the belt and the spine can occur. For this reason bowel perforations have been reported. Many other seat belt injuries have been reported, a few of them are listed below.
Airbags, defective ones that cause shrapnel to impale drivers have caused 24 deaths. Even properly functioning airbags have caused death from myocardial rupture.
TAKE HOME POINTS
1. While restraints are good, they cannot prevent all injuries and they cause some injuries.
2. It’s the deceleration injury that matters. A clue to this is the presence of a “seat belt sign”, associated rib fractures, and ems report of the severity of the crash that help in determining severity. A recent ED case of a patient involved in a crash with negative indications for a head CT but with sternal fracture and pericardial effusion brings this home. The pt was found to have a subdural requiring surgery without striking his head.
Our patient was treated conservatively for her breast injury.
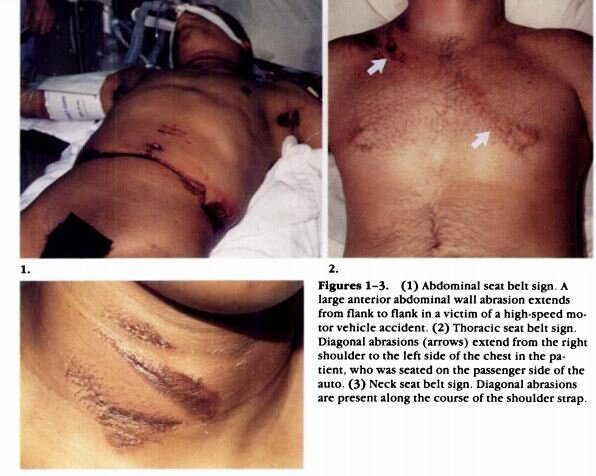
A classic seat belt injury
Campbell B, Porter R, Zhae N. Patterns of safety belt injury reduction related to crash severity and seat position. J Trauma 1987 Jul; 27(7):733-9.
Hayes C, Conway W. et al. Seat belt injuries: radiologic findings and clinical correlation. Radiographics .1991;11:23-26.
Thoma T. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) Notes. Review of studies on pedestrian and bicyclist safety . 1991-2007. Ann Emerg Med. 2012 Oc;60(4):495-6.