Questions of the Week for 5/9/23
Authors: Christian Gerhart and Sam Stringer
1. CMV retinitis is most common in which patient population?
-
Patients with AIDS. Typically patients have a CD4 count <50, can also be seen in other immunosuppressed states especially bone marrow transplant patients.
2. A patient presents with sudden onset, PAINLESS monocular vision loss an hour ago. This patient may be a candidate for what therapy?
-
Thrombolysis. Though this remains controversial, this is considered by some to be a “stroke of the eye” and therefore some authors recommend IV thrombolysis if within 4.5 hours and no significant contraindications.
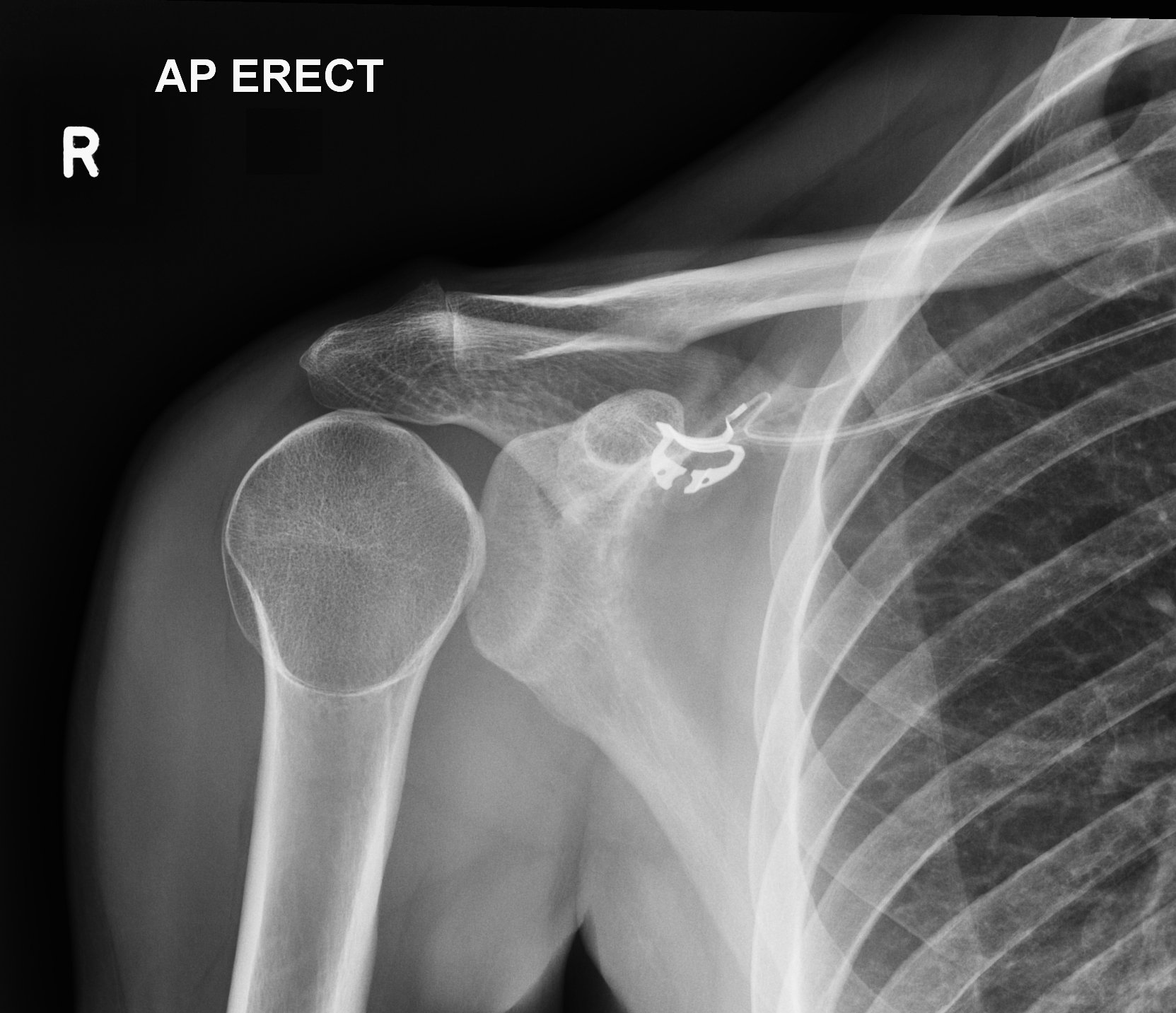
The “lightbulb sign” seen here is indicative of what shoulder pathology?
Case courtesy of Andrew Murphy, <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/?lang=us">Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/46646?lang=us">rID: 46646</a>
-
Posterior shoulder dislocation. It refers to the abnormal internal rotation seen when visualizing the humeral head on the AP X-ray.
4. When examining a lateral elbow radiograph, what findings related to the fat pads are considered abnormal?
-
Anterior: elevation of fat pad which appears as the “sail sign”.
Posterior: any visible fat pad is abnormal. The presence of either indicates a fracture even if no bony pathology is seen.
5. You have a patient with a Boxer's fracture and examine for appropriate finger cascade. Where should the fingers point to? What is the significance of an abnormal finger cascade in the setting of a Boxer's fracture?
-
The fingers should point to the scaphoid bone when performing the finger cascade. Abnormal finger cascade in the setting of a Boxer's fracture indicates malrotation which is an indication for operative management.
6. A patient with previous roux en Y presents with abdominal pain. What unique diagnoses must be considered?
-
A patient with previous roux en Y presents with abdominal pain. What unique diagnoses must be considered?
7. Your patient with a Roux en Y three months ago presents with abdominal pain but has a negative CT. They also endorse some dark stools. What common diagnosis should be considered in this patient?
-
Marginal ulcers. This is fairly common (about 5% of patients who undergo bypass surgery) and can perforate if not diagnosed and managed appropriately w/ PPI. Sometimes ulceration can be so significant it can require revision surgeries.
8. A patient with a recent gastric banding procedure presents with acute abdominal pain and vomiting. What diagnosis must be considered?
-
Band slippage. This can lead to strangulation and perforation if severe. Surgical consultation is always indicated for displacement of gastric bands.
9. What commonly used analgesic should typically be avoided in patients who have previously undergone bariatric surgery?
-
NSAIDS. These patients are at high risk for ulcers, which can be worsened by NSAIDs.
10. Bruising on which areas is always abnormal in children?
-
Torso, Ears, Neck, most facial bruising.