Questions of the Week for 5/2/23
Authors: Christian Gerhart and Sam Stringer
Which bacteria are commonly implicated in causing UTIs but are nitrite negative?
-
Enterococcus, staph saprophyticus. Pseudomonas sometimes produces nitrites but not always.
Treatment for asymptomatic bacteriuria should be considered in what patient populations?
-
Pregnant patients, renal transplant patients or patients with upcoming urologic instrumentation .
You see a hypoechoic structure in the region of the renal pelvis. Besides hydronephrosis, what other structure could this represent and how would you distinguish them?
-
Renal vasculature, can use color to distinguish
Renal or ureteral stones are typically hyperechoic. What phenomenon do they typically exhibit that can help assist in diagnosis?
-
Posterior acoustic shadowing
In appendicitis the appendix typically exhibits what characteristics on ultrasound?
-
Non-mobile, non-compressible, typically >6mm outer diameter
In addition to PRBCs, FFP, and platelets, what other medications or products should we consider administering with our MTP?
-
- Calcium, TXA and cryoprecipitate (fibrinogen)
Most trauma patients in hemorrhagic shock are hypocalcemic AND we are giving them citrated blood products rapidly causing further hypocalcemia which leads to coagulopathy (calcium is factor IV in the clotting cascade) and hypotension, the risk of iatrogenic hypercalcemia from calcium administration is overall low
See the linked resources below from this Siegler guy:
https://emcrit.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/Official-JTACS-Lethal-Diamond.pdf
Name which nerve is tested by each of the following maneuvers: thumbs up, OK sign, peace sign, fist.
-
- Fist: median
- Thumbs up: radial
- 2 fingers peace: ulnar
- A-OK sign: anterior interosseous nerve
A skier lands awkwardly and experiences thumb pain. X rays are negative for fracture. They have pain with abduction. What diagnosis should be considered and how is it managed?
-
UCL ligament tear (gamekeeper thumb), thumb spica splint slightly abducted
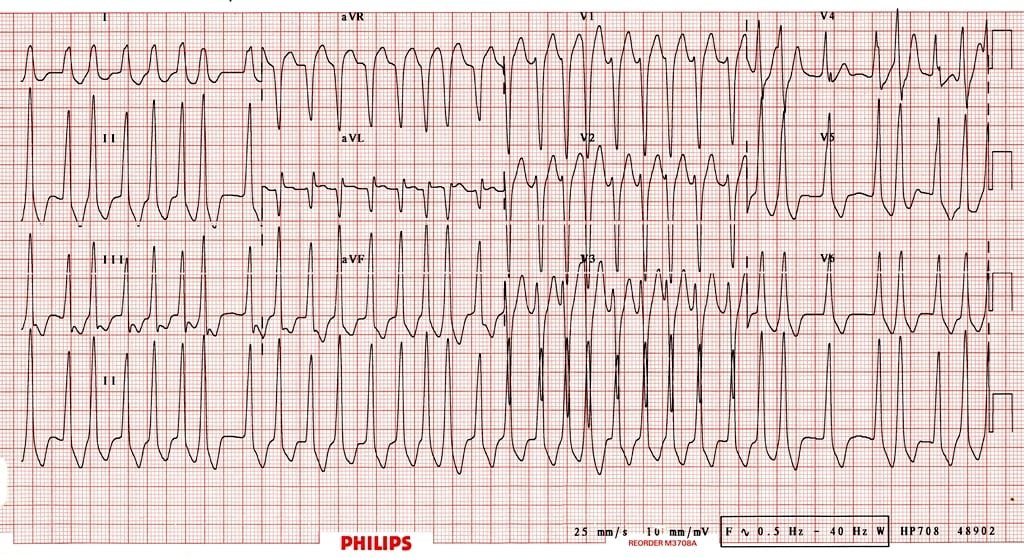
A patient presents to the ED with the following EKG. What is the most likely rhythm and how should this be managed?
EKG from Life in the Fast Lane
-
WPW with atrial fibrillation. Synchronized cardioversion is generally the therapy of choice. Procainamide is the drug of choice though most of these patients will not be stable enough for pharmacologic therapy. AVOID amiodarone/beta blockers as this can increase conduction through the accessory pathway leading to degeneration into ventricular fibrillation.
A pregnant patient presents with Afib w/ RVR with a normal blood pressure. What commonly used medication for atrial fibrillation should be avoided in this patient?
-
Amiodarone, as it is pregnancy class D. If a rate control strategy is preferred, beta blockers are generally appropriate. If a rhythm control strategy is selected propafenone, flecainide or sotalol are generally safe abut should probably only be initiated with cardiology consultation.