A 30 y.o. male comes in with dystonia; involuntary spasms where his head turns right.
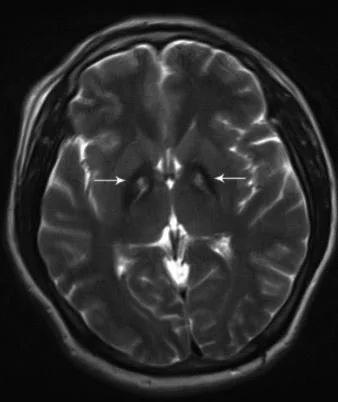
He was seen by neuro who ordered an MRI. It is shown below.
Something is seen in the basal ganglia
A hint is offered in the picture below
Amur tiger at the St.Kouis zoo
Our patient demonstrated an an eye-of-the-tiger sign.
This is a specific magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) pattern on T2 weighted imaging, which consists of a low signal intensity ring surrounding a high intensity signal bilaterally in the globus pallidus. The pattern is often associated with neurodegeneration and iron deposition. In children this deposition is caused by an error in the gene which converts Vit B5 (pantothenic acid) to Co enzyme A (CoA). This is the first enzyme in the pathway that leads to acetyl CoA which is necessary for neural transmission.
Pantothenate kinase 2 (PANK2) -caused neurodegeneration was first described in children with dystonia, choreoathetosis and gait abnormalities. Many also developed vision loss and cognitive decline. When it occurs later in life it often produces dystonia, dysarthria and word repetition. Iron deposition in the basal ganglia is also present in other neurodegenerative diseases with movement disorders including Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, Tourette’s and Huntington’s. As might be expected since iron is a sign of neurodegeneration. it is also found in other parts of the brain in many neurodegenerative diseases. In Alzheimer’s it is found in the hippocampus and temporal lobes associated with memory loss. In normal aging, iron deposition in the caudate is associated with difficulties with balance.
A REVIEW OF VITAMIN B
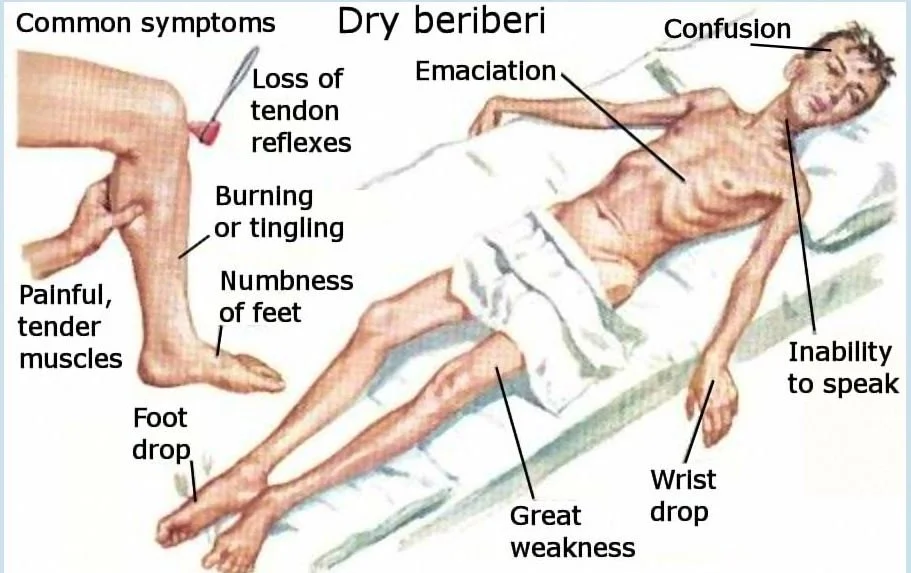
B1 thiamine- thiamine deficiency or beriberi presents in multiple ways
B2 riboflavin- riboflavin deficiency causes cheilosis, angular stomatitis and glossitis along with vision problems
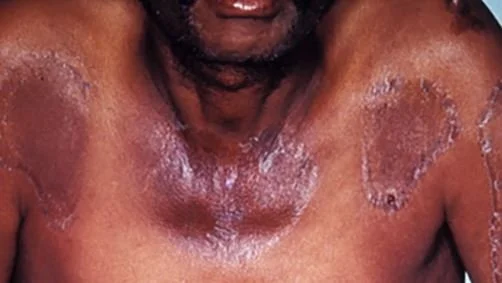
B3 nicotinamide, nicotinic acid- is also known as pellagra and is associated with the four D’s: dermatitis, diarrhea, dementia and death.
dermatitis in pellegra
B4 adenine- found in bee pollen, a component of DNA and RNA
B5 pantothenic acid- important in the formation of steroids and causing adrenal insufficiency when deficient. Is also synthetized by E. coli and Salmonella in the gut. vitamin B5 was named for Pan derived from the Greek word pantos meaning everywhere. It is ubiquitous in food and deficiency is only found in those with severe malnutrition or genetic abnormalities. . It plays a role in neurodegeneration and it has been found to be deficient in patients with Huntingtons.
B6 pyridoxine- is also produced by gut bacteria. Deficiency is associated with peripheral neuropathy and burning, blistering skin.
B7 biotin-essential for carbohydrate and fat metabolism. A deficiency of biotin is rare but can result in hair loss and seizures.
B8 inositol-produced from carbohydrates
B9 folic acid- Deficiency often presents with anemia and a smooth red tongue.
B10 para amino benzoic acid PABA- synthetized in the gut
B11salicylic acid- can be synthetized in the body and found to be high in vegetarians
B12 cobalamin- common symptoms of deficiency include macrocytic anemia and fatigue It should be tested with folate.
In addition to neuro-degeneration in the globus pallidus, our patient suffered from dystona an associated involuntary movement disorder. . He had spasms of the neck causing the head to be turned to the right. He was treated with Botox injections. 40% of individuals with dystonia never learn the cause.
FUN FACTS
So what happened to Vit B4,8,10 and 11? They no longer meet the definition of a vitamin since they are not essential nutrients that the body cannot synthesize.
Vocal dystonia or spasmodic dysphonia causes spasms of the larynx which results in interruptions in the voice. Robert F Kennedy Jr. has vocal dystonia.
Iron chelation is currently being investigated to treat neurodegenerative diseases.
Chang C, Ming-Lin C. Eye -of-the Tiger sign is not pathognomonic of pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration in adult cases. Brain Behav 2011 Sep;1(1:55-56.
Orellana D, Santambrogio P, Rubin A et al. Coenzyme A corrects pathological defects in human neurons of PANK2-assocaited neurodegeneration. EMBO MolMed. 2016 Aug 11;8(10):1197-1211.
Wan Z, Zheng J, Zhu Z, et al. Intermediate role of gut microbiota in vitamin nutrition and its influences on human health. Fron Nutr. 2022 Dec 13;9:1031502.
Cummings J. The large intestine. its role in mammalian nutrition and homeostasis. Quart Rev Biol. (1981) 22:896–901.
Ranganath P, Patil M. Eye of the tiger: looking beyond neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation disorders. J Pediatr Genet. 2021 Feb 17;12(2):163-166.
Dusek P, Hofer T, Alexander J, et al. Cerebral iron deposition in neurodegeneration Biomolecules. 2022 May 17;12(5)): 714.