A 55 y.o. woman presents with a rash and chronic diarrhea.
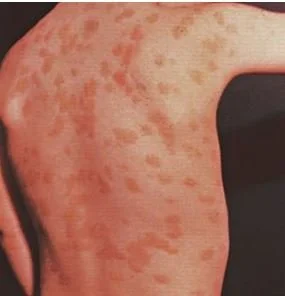
The rash consists of reddish brown plaques.
Stool for O +P, stool culture, C diff screening, alpha feto protein and liver functions were all unremarkable. What is in your differential?
Our patient had systemic mastocytosis with involvement of the skin, gut and bones.
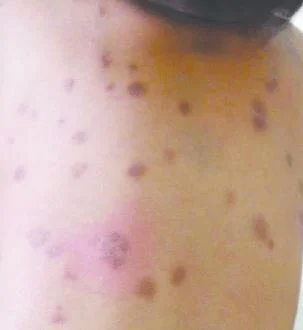
The condition was first described in 1869 by Nettleship and Tay and due to the appearance of an urticarial rash it was called urticaria pigmentosa. Research has shown that mutations in the KIT gene are the cause. The skin condition is marked by brownish red lesions which become urticaria after gentle rubbing. (Darier’s sign)
rubbing a lesion will create an urticarial reaction
There is a spectrum of mast cell disease. The diseases ranging from cutaneous mastocytosis to mast cell tumors and mast cell leukemia .
Cutaneous mastocytosis is often in children and tends to regress with age. It usually does not spread to organs.
Systemic mastocytosis occurs more frequently in adults. There is involvement of the organs including bones and gut . This is caused by a clonal proliferation of mast cells. Mast cells are capable of releasing mediators including histamine, leukotrienes and cytokines. Tryptase is often elevated. The mediators can cause chronic diarrhea, flushing, and abdominal pain They can also present with sudden massive mediator release causing anaphylaxis. The diagnosis of systemic mastocytosis is confirmed by bone marrow biopsy and tryptase.
sclerosis of the spine caused by systemic mastocytosis
Mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS) is a secondary mast cell reaction in which there is inappropriate activation of a normal number of mast cells leading to symptoms. Since mast cells are activated in many common conditions, it is a difficult diagnosis to make and first other causes for mast cell activation must be ruled out. . IgE related food allergies, carcinoid syndrome, vipoma, gastrinoma and even exercise can present with mast cell activation. Studies have shown only 2-4% of people who diagnose themselves ( with the help of chatGPT) as having MCAS actually have mast cell activation. Therefore, the American Society of Allergy and Immunology in 2025 published criteria for making the diagnosis.
1. Episodic activation of two different organ systems must be present during symptoms. An example would be low BP and a rash or abdominal pain and fatigue.
2. Objective criteria must be present. The tryptase level must be >8 nanograms/ml or increase from baseline by 20% during a symptomatic period. This must tested in 4 hours of symptom onset.
3. Antihistamines or leukotriene inhibitors must relieve the symptoms.
Our patient had systemic mastocytosis confirmed on biopsy. She received an epipen and treatment for bone involvement is with midostaurin, a KIT inhibitor. After treatment her skin lesions and diarrhea resolved.
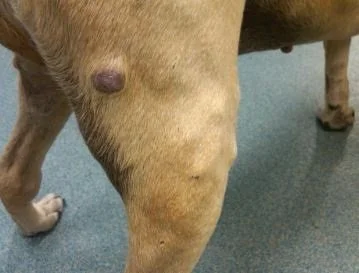
A dog with mast cell tumors
FUN FACT
Dogs also get mast cell tumors. About 20% of skin cancers in dogs are mast cell tumors. They are thought to have a genetic predisposition and are more likely to occur in boxers, bulldogs and Boston terriers. They can can be very aggressive and grow quickly resulting in rupture.
Hamera L, Santos A, Prince S, et al. Systemic mastocytosis: a rare cause of diarrhea. Cureus . 2020 Jul 10;12(7):e91112.
Zanelli M, Quintini M, Magnasco S, et al. Mast cell leukemia: an update with a practical review. 2023. Cancers(Basel) Mar 8;15(6):1664.
Srinivas S, Dhar S, Parikh D. Mastocytosis in children. Indian Journal of Paediatric Dermatology. 2015 April-June vol 16(2).
Management of indolent mastocytosis and mast cell activation syndrome-a clinical yardstick. Journal of Allergy and Immunology. 2025. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vCGqa30TPjg
Neves da Silva L. Montero A. Systemic mastocytosis . NEJM Sept 25”1215/