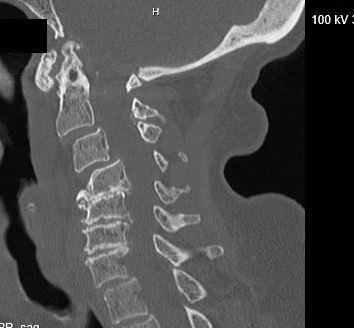
A 79 y.o. woman with a hx of R sided weakness fell forward on to her face.
Would you clear her c-spine?
Our patient had a severe cord injury. MRI showed a disruption of the anterior longituginal ligament. She had edema in the interspinous ligaments and a significant prevertebral hematoma. She also had severe spinal canal stenosis with cord edema from C4- C7. There was hemorrhage within the cord at C4. There was no bony fracture.
within the spinal cord there is white signal on this T2 weighted images; above the arrow the cord is normal.
Putting this together, the patient’s old R sided weakness was most likely from cervical myelopathy not an old stroke. The case offers a chance to review normal C spine anatomy and cervical myelopathy.
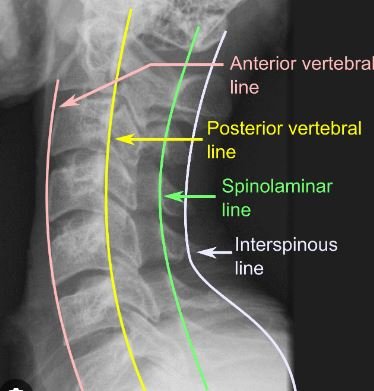
On plain film, a normal C spine can be thought of as a series of lines that represent the normal position of the cervical vertebra. These lines include the anterior vertebral line, the posterior vertebral line, the spinolaminar line and the interspinous line.
As normal aging takes place bony changes develop as cervical discs dessicate , which can cause cord compression. Osteophytes and facet hypertrophy contribute to canal narrowing.The whole process of loss of the discs and development of arthritis is referred to as cervical spondylosis. 85% of people older than 60 have cervical spondylosis. If the canal is narrowed by more than 60%, myelopathy , muscle weakness will develop.
changes of cervical spondylosis
The tracts most frequently affected are the lateral corticospinal tracts(voluntary muscle control ) and the spinocerebellar tracts (proprioception). These deficits cause a wide-based spastic gait with clumsy upper extremities. Lhermitte’s sign (positions that create an electric shock down the back) or urinary incontinence are later more serious signs and imply a poor prognosis.
Cervical myelopathy (muscle weakness) is defined as a compression of the spinal cord at the cervical level resulting in spasticity, hyperreflexia, hand clumsiness or gait disturbance If the canal is narrowed by more than 60%, muscle weakness will develop. The tracts most frequently affected are the lateral corticospinal tracts(voluntary muscle control ) and the spinocerebellar tracts (proprioception). These deficits cause a wide-based spastic gait with clumsy upper extremities. Lhermittes sign (positions that create an electric shock down the back or urinary incontinence are later more serious signs and imply a poor prognosis.
Undiagnosed cervical myelopathy was found in 18% of patients presenting with a femur fracture.
As our population ages it is important to consider cervical spondylosis in our patients with falls. This is Anthony Hopkins as Methusaleh, who was reportedly 969 years old.
The initial xray was read as “degenerative changes of the c spine with no fractures. “ She was treated in the ED as though she had a c-spine injury.
She developed quadriplegia and goals of care were discussed. Care was withdrawn and she expired.
Radcliff K, et al. high incidence of udiagnosed cervical myelopathy in patients with hip fracture compared tocontrols. J orthop Trauma doi:10.1097/BOT.000000000000485/
Connallly C, Butler A, Rush A, et al. the most influential publications in cervical myelopathy. J Spine Surg 2018 Dec ;4(4):770-779.
Expert Panel on Neurological imaging. Mcdonald M, Kursch C, Amin B, et al. ACR Appropriateness criteria Cervical neck Pain or Cervical Radiculopathy J Am Coll Radiol 2019 May;16(5S)S57-S76.
Machino M, Ando K, Kobayashi K, et al. Cut off value in each gender and decade of 10-s grip and release and 10-s step test . A comparative study between 454 patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy and 818 healthy subjects. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019 Sep 184:105414.