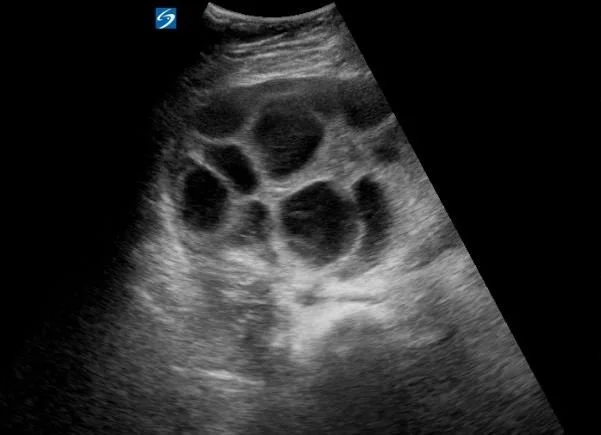
A 22 y.o. woman presented with RLQ pain and ascites.
An US was done in the ED
Hint: the pt is receiving LH injections as part of her infertility treatment.
Our patient had ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome caused by her fertility treatments and presented with ascites and pain.
Clomiphene(clomid) was created in 1956 to treat oligomenorrhea but was expanded to treat anovulation when patients undergoing treatments were found to have higher than normal rates of pregnancy. Trials were also conducted in patients with advanced breast cancer but these were abandoned because of side effects like irreversible cataracts because of its effects on cholesterol metabolism .
The purpose of giving Clomid in infertile pateints is to stimulate egg production. it works by binding to estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus that would normally be occupied by estrogen; making estrogen levels “appear low”. As a result the hypothalamus signals the pituitary to increase FSH production which causes an increase in ovarian follicles and increases estrogen.
Ovarian hyperstimultation syndrome is more likely if HCG is given or occurs naturally in the luteal phase
The problem occurs when greater than 20 follicles are produced. Large volumes of ascites can be produced because of increased capillary permeability( increased vascular endothelial growth factor) causing pain, respiratory distress and oliguria. If the volume of ascites is large enough, pleural effusions develop. Complications of renal failure and DVT can also result. About 2% of patients that receive drugs to stimulate the ovaries develop ovarian hyperstimulation. The risk factors include: polycystic ovaries, high follicle count and elevated serum estradiol. Stimulation protocols using hCG for luteal phase support also increase the risk.
pleural effusion in a patient with ovarian hyperstimulation
Although ovarian hyperstimulation is associated with fertility treatments, it has also been reported in hypothyroidism, pregnancies with multiple gestations and trophoblastic disease.
an 18 yo with spontaneous ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. She had an abortion at 10 wks.
FUN FACT: an “epidemic” of twins and triplets began after clomid was introduced since in a normal singleton pregnancy one mature follicle will suppress other follicle formation but this does not occur with clomid. You are up to 12x more likely to have twins on clomid and 1 % more likely to have triplets.
Reefhuis J, Honein M, Schieve L, et al National Birth Defects Prevention Study. Use of clomiphene citrate and birth defects, Nationl Birth Defects Prevention Study, 1997-2005. Hum Reprod. 2011;26(2):451-7
Al-Ramahi M, Leader A, Claman P, Spence J. A novel approach to the treatment of ascites associated wwith ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Human Reproduction 1997. Volume 12 , Issue 12.
Grossman L, Michalakis K, Browne H, et al. The pathophysiology of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: an unrecognized compartment syndrome. 2010 Fertil Steril Sep;94(4):1392-98.
Yildizhan R, Adali E, Kolusari A, et al. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome with pleural effusion: a case report. Cases J. 2008;1:323.
Nastri C, Ferriani R, Rocha I, et al. Ovarian hyperstimultaiton syndrome: pathophysiology and prevention. J Assist Reprod Genet 2010Feb;27(2-3):121-128.
Sridev S, Sridev B. Case report on spontaneous ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome following naterual conception associated with primary hypothyroidism. J Hum reprod Sci. 2013 Apr-Jun;6(22):158-161.