A 27 y.o. woman injected subutex into her radial artery. One hour later she came to the ED complaining of hand pain.
What happened? Hint: initially there was no radial pulse but a strong ulnar; the radial pulse returned in one hour.
her hand was swollen and she developed a rash on the forearm.
sensation , motor function, and cap refill was intact.
Our patient developed a compartment syndrome of the thenar eminence of the hand. Compartment syndrome is a condition that can be easily missed with because is can present with delayed symptoms. This is especially true in patients with a history of opiod use. On clinical exam, increased pressure in the compartment, pallor and pulselessness are red flags. Although the five “P’s” are taught as signs of a compartment syndrome (Pain, Pallor, Pulseness, Paresthesias, and Paralysis) In addition, a compartment pressure of 30 provides objective support for the diagnosis of compartment syndrome.
A meta-analysis of clinical studies found that the positive predictive value of the clinical findings was 11-15%. So how do you prevent a diagnostic error?
The best indication of compartment syndrome is “pain out of proportion”. Pain caused by ischemic tissue is intense and surpasses what would be thought of as normal for the injury.
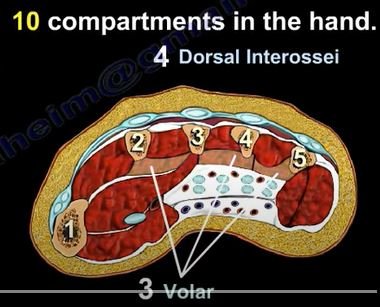
10-11 compartments exist in the hand
Our patient underwent fasciotomy of the thenar compartment.
the thenar compartment
This is not a new problem. Richard von Volkmann in 1881 published an article describing irreversible contracture of the flexor muscles of the hand because of ischemic processes in the forearm. Intramuscular pressure is elevated to a point which reduces capillary perfusion causing muscle ischemia
Often a compartment syndrome occurs with trauma and it can be a mistake to attribute the patient’s pain solely to the underlying fracture. Tibial fractures are the most common cause of compartment syndrome followed by distal radius fractures. Seventy-five percent of cases of acute compartment syndrome are associated with fractures. Multiple other causes are listed below.
Our patient was taken to surgery. In addition to fasciotomy of the thenar compartment she had a release of the median nerve.She recovered successfully.
Ulmer T. The clinical diagnosis of compartment syndrome of the lower leg: are clinical findings predictive of the disorder? J Orthop Trauma 2002;16(8):572-7.
Chandraprakasam T, Kumar R. Acute compartment syndrome of the forearm and hand. Indian Journal of Plastic Surgery: Official Publication of the Association of Plastic Surgeons of India. 2011May-Aug;44(2):212-218.
Duckworth A, McQueen M. “Focus on: diagnosis of acute compartment syndrome, The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery—British Volume, pp1-8, 2015.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NNiIKzoWVFk