An 84 y.o. presents to the ED with pain over his tailbone and down the L leg.
An xray was done in the ED.
Hint: the xray was read as mild hip OA; what could be wrong.? He was given a lidocaine patch and sent home with referral to spine
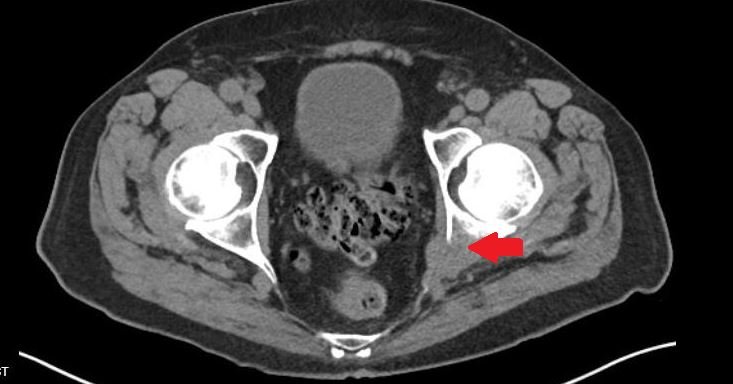
Our patient returned three days later with the same complaint. He was unable to walk and a CT was done to look for occult fracture.
CT showed a lesion in the L ischium
What is the differential for hip pain in the elderly?
Among adults older than 60 years, 14% report hip pain intermittently often due to osteoarthritis but there are many other causes. In general, if the patient cannot walk, further testing is needed beyond plain films. A history of trauma, failure of four weeks of treatment, intermittent locking of the hip or hip deformity are red flags requiring further imaging.
OCCULT FRACTURES- hip radiography can miss fractures > 10% of the time. Multiple studies have shown MRI or CT is needed for persistent pain. Avascular necrosis and labral tears cannot be diagnosed on xray.
MUSCULOSKELETAL CAUSES: trochanteric bursitis, iliopsoas bursitis, piriformis syndrome, referred pain from the knee or spine
A labral tear can be extremely painful
METASTATIC TUMOR- Cancers most likely to spread to bone are breast , kidney, lung, prostate, thyroid multiple myeloma and lymphoma.
SACRAL INSUFFICIENCY FRACTURES- are a type of stress fracture resulting from normal stress applied to a bone with reduced elasticity. Osteoporosis or Paget’s disease are common causes. 85% will heal in 12 weeks.
sacral insufficiency fractures are stress fractures and can occur without trauma
SI JOINT ARTHRITIS- 15% of low back pain is due to SI joint arthritis. RA, lupus, ankylosing spondylitis and gout have all be implicated. In younger people, reactive arthritis caused by an STD can occur months after the infection.
INFECTION- In addition to prosthetic joint infections, staph infections gram negative rods like salmonella, and pseudomonas can be found in native hip infections.
echinococcal infections can occur in the SI joint
Our patient had a remote history of prostate cancer treated with proton beam. A biopsy was done of the L ischium which was thought possibly to be prostate ca but it showed a neuroendocrine tumor of unknown primary. It was polyphenotipic and multiple lesions were found in the R sixth rib and liver. He has been too weak to make any return appointments and chemo is not anticipated.
Schon L, Zuckerman J. Hip pain in the elderly: evaluation and diagnosis. Geriatrics 1988 Jan;43(1):48-62.
Smith J, Jenkin A, Hennessy C. A retrospective chart review of elderly patients who cannot weight bear following a hip injury but whose initial xrays are normal. Emerg Med J. 2009;26(1):50-51.
Geipel U, Pathogenic organisms in hip joint infections. International Journal of Medical Sciences 2009;6(5):234-240.
Kayya H, Kerimoglu U. Case 269: Sacroiliac Joint Hydatid Disease. Radiology 2019;292:776-780.