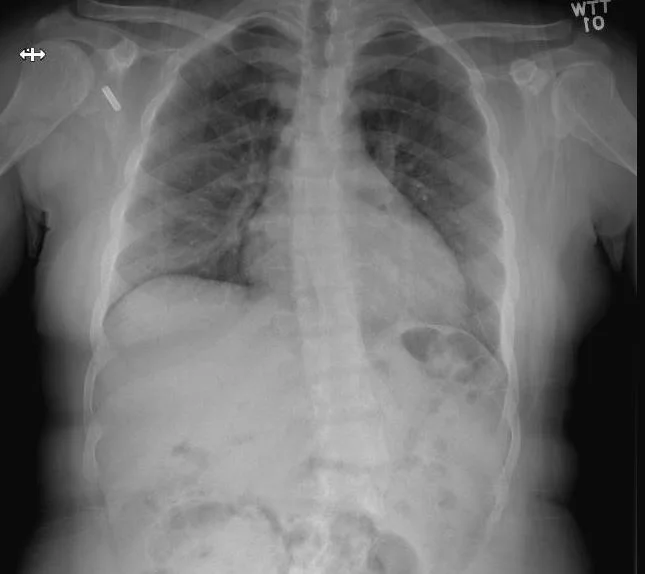
A 22 y.o. woman presents to the ED with low back pain after a fall in the bathtub. Her cxr and bone scan are shown.
What is wrong?
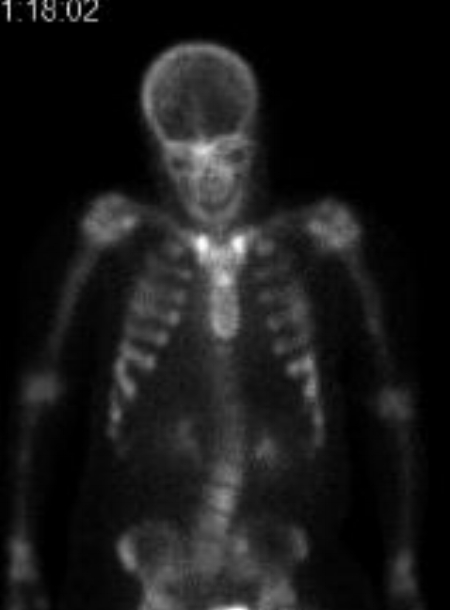
bone scan
Our patient had rickets with the classic “tie” sign ; increased uptake over the sternum on bone scan.
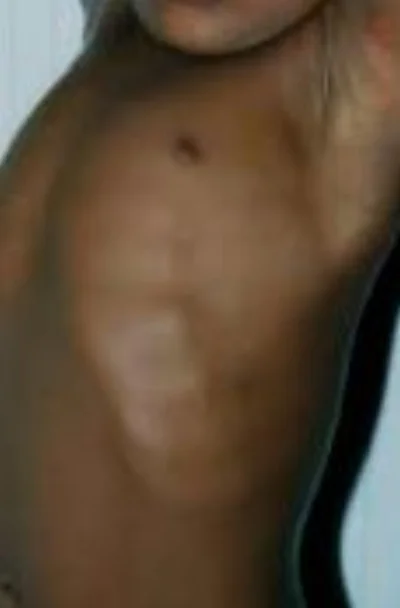
Rickets results from defective mineralization or calcification of bones due to deficiency or impaired metabolism of Vit D, Mg, phosphorus or calcium. If this occurs prior to epiphyseal closure in children bony abnormalities result. These include bowing of the femurs, scoliosis, and skull bossing.
Rickets was first described in Ephesus in the first century AD when Soranus described it in infants. In 1645, Whistler in England defined it as a specific medical condition. It wasn’t until 1923 thatSteenbock in the US showed that irradiation of food couldincrease the amount of Vitamin D and reverse the disease. Rickets was nearly eliminated from the US by 1945 due to the irradiation of milk.
Bowed legs
There are several types of rickets.
1. The most common is Vit D deficient, which is caused mainly by malnutrition often in the mother who is then unable to provide Vit D in her breast milk.
Vit D responsive rickets persists in the rest of the world. The Middle East, despite high rates of sun-exposure has the highest rate of rickets worldwide. This is explained by limited sun exposure due to cultural practices and lack of Vit D supplementation in nursing women. 80% of girls in Iran and Saudi Arabia are Vit D deficient.
2. Our patient had a second type of rickets ; Vit D resistant rickets or X linked hypophosphatemia. This is a mutation in the X chromosome causing overactivityof fibroblast growth factor and decreased phosphate resorption by the kidneys.
3. A third type of rickets is caused by fibroblast tumors. In these individuals a tumor produces fibroblast growth factor and decreased absorption of phosphate in the kidneys. In these cases removal of the tumor cures the disease.
swollen costchondral junctions; the rachitic rosary
Our patient had scoliosis and multiple microfractures on bone scan. On her current ED visit plain films showed no new fracture in the back and she was given symptomatic treatment.
Imaging in all types of rickets shows pseudofractures which light up on bone scan where there is a stress fracture caused by insufficient mineralization. They tend to occur bilaterally in the mandible, at costochondral junctions ( causing the rachitic rosary) andin the epiphyses of the knees.
The Middle East & Africa Regional Audit Executive Summary, epidemiology, cost & burden of osteoporosis in 2011. The International Osteoporosis foundation. www.iofbonehealth.org.
Magnesium and vitamin D’s co-factors, by John Jacob Canell, MD. Citing The Lancet: The Vitamin D Council. Two cases of Mg dependent Vit D resistant rickets appeared in the Lancet in 1974.
Pettifor JM 2004. Nutritional rickets : deficiency of vit D, calcium, or both?. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (Review) 80(6 suppl): 1725S-9S.