A 70 y.o male who wears contact lenses comes to the ED with a red eye and loss of vision.
The pupil reacts normally, the Wood’s lamp exam is normal, the pressure is 22 and the posterior pole is normal on US. He can see only shapes. What is wrong?
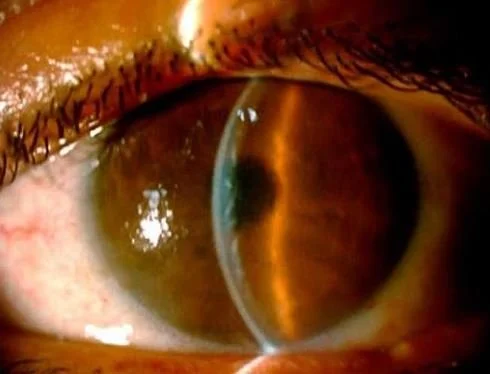
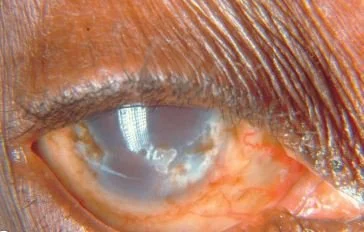
this is his cornea on slit lamp exam
Our patient had corneal edema with microcysts on the cornea. These are often not visible with fluorescein because hypoxia occurs first at the deepest layers of the cornea, near Descemet’s membrane. Hypoxia is a well described complication of contact lenses; especially in those who wear “extended-wear” contact lenses.
With corneal edema Descemet’s membrane can buckle causing the whitish patches seen here.
The cornea depends on the atmosphere and tears for its oxygen supply. Contact lenses form a barrier to atmospheric absorption of oxygen. This can lead to corneal hypoxia which can present as a red painful eye, blurred vision, loss of vision, or swelling around the eye.
CAUSES OF CORNEAL EDEMA
Contact lenses- especially extended wear are the number one cause. This can be limited to the cornea alone leaving the posterior pole unaffected. Acanthamoeba is an infection found mainly in contact lenses wearers.
Infection-bacterial and viral including Tbc, syphilis, Lyme disease. Here the damage is not just to the cornea; but can cause a pan uveitis ( Inflammation of the entire eye) Herpes is one of the infections that can cause corneal edema even years after the initial episode of infectious keratitis. Parasites can also cause corneal edema.
River blindness ( onchocerciasis) affects the cornea
Uveitis due to immune diseases- HLA-B27 associated entities, MS, Behcet’s, sarcoidosis and lupus. In addition to cell in the anterior chamber corneal edema can result.
Environmental causes- Ultramarathon runners frequently experience corneal edema from wind and cold. Chemical burns, increased pressure from glaucoma, and trauma can all produce corneal edema. It occurs routinely after cataract surgery.
Drugs- amantadine, amiodarone, antimalarials and even ibuprofen
While the original ED exam was thorough; the diagnosis was missed because a slit lamp exam was not performed. Edema initially causes the cornea to have a dull appearance. As the edema persists, the cornea may develop microcysts , bullae and scarring. If untreated a cornea transplant could be necessary.
The patient was treated with 5% hypertonic tear film, drawing water out of the cornea. He was also given a steroid. The vision cleared within four days
FUN FACT
In the UK there are more cases of acanthamoeba corneal involvement than in the rest of Europe combined. This is thought due to the fact that most homes have water storage tanks in the loft supplying the bathroom while the kitchen water comes from the main line. In Europe, all water comes from the main lines. So if you rinse your contacts in the bathroom in the UK, where the water is from a tank that may harbor acanthamoeba, the risk of contamination is real.
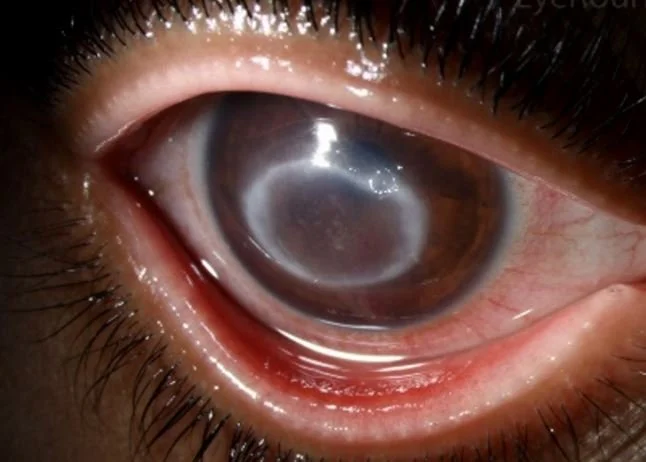
circular corneal lesion from ancanthamoeba
Galor A, Jeng B, Lowder C, et al. A curious case of corneal edema. EyeNet magazine Jan 2007
Fei L, Yang R, Yang L, et al. Acute foggy corneal epithelial disease: seeking clinical features and risk factors. JCM 2022 Vol 11(17)
Urrego-Diaz J, Frias-Ordonez J, Figueroa-Enchandia. Acute corneal edema without epithelium compromise. A case report and literature review. Medicina 2016
Hsu Y, Huang J, Tao Q, et al Noninfectious uveitis in the Asia-Pacific region. Eye(Lond) 2018 Oct 15;33(1):66-77.