A 28 yo woman comes to the ED with a complaint of vision loss and weakness
She had been seen one week earlier for hypokalemia and treated. She currently is dehydrated with ketones in her urine and has altered mental status . She has temporal vision loss in one eye. MRI and LP were negative.
the small square is the physiologic blind spot toward the temporal side.
The visual field above is a representation of what she could see. Knowing that bitemporal hemianopsia locates to the optic chiasm, what could be causing her vision loss.
Our patient had a nutritional optic nerve injury. The hint here is that it must be something in the optic nerve. She had a central scotoma and loss of vision in the temporal field which is supplied by the posterior optic nerve where it joins the chiasm. She had a history of heavy alcohol intake and poor food intake with documented folate deficiency. She had not had alcohol in two weeks but weakness and nausea kept her from eating.
optic neuropathy can appear with disc edema as on the L or disc pallor on the R
Almost all patients complain of a blurring or dimness of vision and of difficulty in reading small print. Occasionally patients may complain of difficulty in differentiating red from green. Eye pain can be reported with moving the eye from side to side.
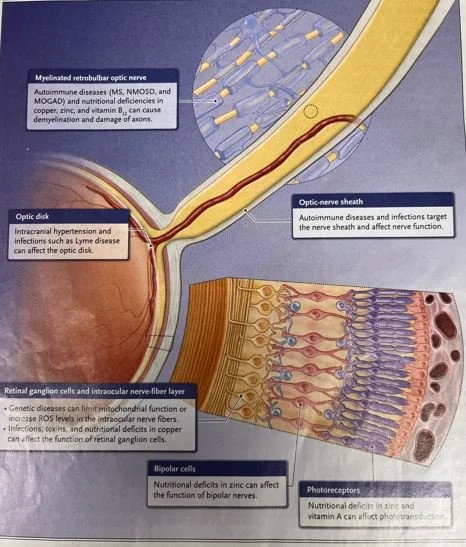
Nutritional deficiencies and toxic optic nerve injury often co exist. The term used for this is toxic amblyopia. Alcohol tobacco optic neuropathy occurs mostly in middle aged men. Vit B12 deficiency affects middle aged women particularly of Scandinavian descent. A brief list of the causes of optic neuropath follows.
CAUSES OF OPTIC NEUROPATHY
NUTRITIONAL DEFICIENCIES-central vision is most often affected with nutritional deficiencies. Vit A ,B12, copper and zinc deficiencies have been associated with vision loss.
AUTOIMMUNE OR INFLAMMATORY- optic neuritis is associated with multiple sclerosis. Inflammatory optic neuritis can occur in sarcoid or ANCA associated disease.
GENETIC -optic nerve deterioration occurs over a much slower time course than in this patient. Lebers hereditary optic neuropathy is autosomal dominant and appears in young adults.
TOXINS- multiple toxins including alcohol/tobacco, linezolid, ethambutol, chloroquine, amiodarone, and lead have been implicated in optic neuritis. Sildenafil has also been implicated.
NEJM article showing where the damage occurs in different types of optic neuritis.
DID YOU KNOW?
50,000 cases of optic and peripheral neuropathy were reported in Cuba between 1991-3. This was linked to nutritional intake and thought to be from a deteriorating economic situation decreasing food availability.
Recently Katz reported in the JAMA journal of ophthalmology (Jan 30,2025) 7 diabetics taking GLP-1 receptor agonists developed optic neuropathy (NAION).
Our patient was lost to follow up.
Prakash J, Ryali V, Srivastava K, et al. tobacco-alcohol amblyopia: a rare complication of prolonged alcohol abuse. Ind Psychiatry J. 2011 Jan-Jun;20(1):66-68.
Sharma P, Sharma R. toxic optic neuropathy Indian J Ophthalmol 2011 Mar-Apr;59(2):137-141
Gaier E, Jairnes C, Gise R, et al. Case 25-2024: A 12-Year-Old Boy with autism and decreased vision. NEJM 2024;391641-650.
Keitner J, Johnson C , Cello K, et al Visual field profile of optic neuritis. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010 Mar;128(3):330-337.
Anderson C, Blaha G, Marx J. Humphrey visual field findings in hydroxychloroquine toxicity Eye 2011 25, 1535-45