A 35 y.o. woman with no medical history comes to the ED with shortness of breath
Paramedics report there was a pan on the stove which was scorched. Her temp was 38.2 and O2 sat was 90%. The key to the diagnosis is shown below.
What was wrong?
Our patient had polymer fume fever.
A condition described as metal fume fever has long been described in welders but polymer fume fever is a distinct entity related to the heating of polymers attached to metal. Polymer fume fever is also known as teflon flu. The fumes are released when PTFE(polytetrafluroethylene) reaches temperatures of 300 degrees Centigrade. Our patient was heating water on the stove and fell asleep causing the pan to overheat.
Teflon is a fluorocarbon product that was discovered by accident in 1938. Researchers at DuPont found that tetrafluoroethylene gas polymerized with metallic canisters forming a friction free non- stick surface. Telfon is used in stent coatings, hernia meshes and-water resistant fabrics like Gortex.
It’s degradation products produce a flu-like illness with sob, cough and fever. In significant exposures pulmonary edema can occur but most patients recover in two to three days without treatment. In cases of pulmonary edema, neutrophil elastase inhibitors have been used to increase IL-8 reducing the inflammatory response.
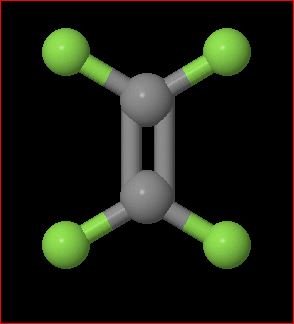
The teflon monomer has four fluorine atoms which would rather attach to other fluorine atoms. This causes them to form long chains called polymers. They do not bind easily to other compounds which makes them perfect for non-stick pans
FUN FACTS
While the most common cause of polymer fume fever is leaving a teflon pan on the stove, other cases have been reported.
Teflon coated heating bulbs in a chicken breeding facility killed 60 of 65 birds . They all suffered from pulmonary edema.
Much like the “ canary in the coal mine” ; there is a report of four cockatiels killed by teflon fumes from an overheated pan. The owner had polymer fume fever.
Our patient recovered without treatment in two days. The teflon pan was unusable.
Hamaya R, Ono Y chida Y et al. Polytetrafluoroethylene fume-induced pulmonary edema:a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case rep 2015 May 14;9:111.
Greenberg M, Vearrier D. Metal fume fever and polymer fume fever. Clin toxicol(Phila)2015 May;53(4):195-203.
Harris D. Polymer-fume fever. Lancet. 1951 Dec 01;2(6692):1008-11.
Lee N, Baek K, Park S, Hwang I, Chung I, Choi W, Jung H, Lee M, Yang S. Pneumoconiosis in a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) spray worker: a case report with an occupational hygiene study. Ann Occup Environ Med. 2018;30:37.
Blandford T, Seamon P, Hughes R. A case of polytetrafluoroethylene poisoning in cockatiels accompanies by polymerfume fever in the owner. Vet Rec. 1975 Feb 22;96(8):175-8.
Full disclosure: My summer job in college was in a teflon spraying line at Nordic Ware in Minnesota. At the time OSH was investigating the possibility of lung disease among the employees. Granulomatous lung disease has since been confirmed in teflon workers.