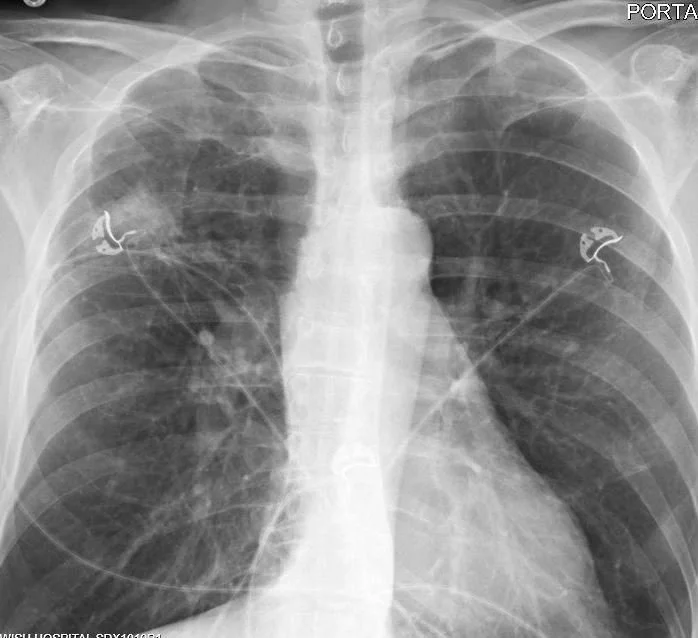
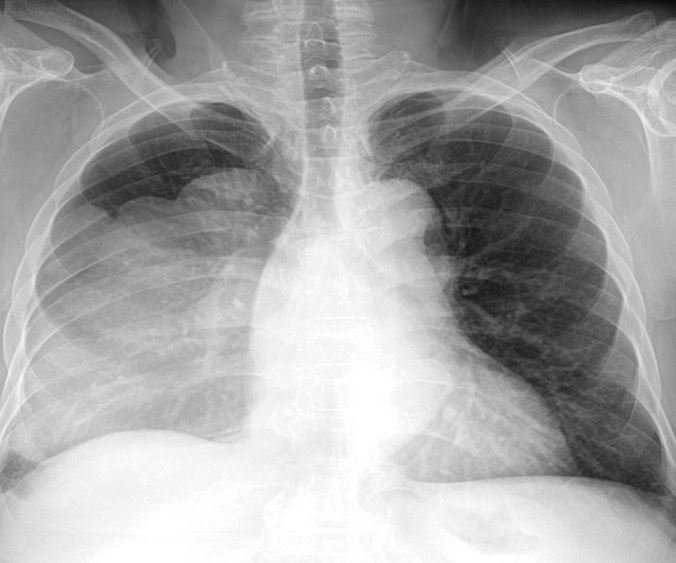
A 54 y.o. male, with a history of lung cancer, comes in with nausea and vomiting. His cxr is shown below.
He is in DKA with no history of diabetes; can you predict what chemo he is taking?
Our patient was on a check point inhibitor for his lung cancer which can cause DKA even if the patient is not diabetic. These drugs can cause an autoimmune diabetes and other autoimmune conditions.
Check point inhibitors are monoclonal antibodies which restore antitumor immunity( reversing the ability of tumors to escape the immune system attack) and cause tumor death. Unfortunately, autoimmunity increases and multiple autoimmune conditions may result. These drugs include PD-1 inhibitors (nivolumab, pembrolizumab, cemiplimab) and PD-L1 inhibitors (atezolizumab, avelumab, duravalumab) and CTLA-4 inhibitor(ipilimumab).
Above is a picture of autoimmune conditions caused by check point inhibitors.
The most common autoimmune conditions caused by check point inhibitors are rashes, hypophysitis, thyroid disease and adrenal insufficiency. Since check point inhibitors are approved for many types of tumors, it is important to be aware of their complications. A partial list of tumors approved by c the FDA for heck point inhibitors is listed below.
Diabetes is permanent and in the case of our patient required relatively high does of insulin. He was given 25 units of glargine qhs and 18 units of lispro with meals. plus a correction scale. Our patient was also hyperthyroid and was treated with methimazole and propranolol. He was discharged with oncology follow up.
FUN FACT
A lung cancer can also cause hypoglycemia as in the case of a solitory fibrous tumor of the pleura:Doege-Potter syndrome. IGF-II is produced by the tumor. This is a benign tumor.
Akturk H, Michels A. Adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a new era in autoimmune diabetes. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabete Obes. 2020 Aug:27(4)187-193.
Aturk H, Michels A. Adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade. NEJM 2018;378:1163-4
Martins F, Sofiya L, Sykiotis F, et al. Adverse effect os immune-checkpoint inhibitors:epidemiology, management and surveillance. Nature reviews clinical oncology 2019,16,563-580
Yin Q, Wu L, Han L, et al. Immune-related adverse events of immune checkpoint inhibitors: a review. Fron Immunol 2023;14:1167975
Fukasawa Y, Takada A, Tateno M, et al. Solitary fibrous tumor of the pleura causin recurrent hypoglycemia by secretion of insulin-like growth factor II. 1998 Vol 48(1) 47-52.