A 61 y.o. alcoholic comes in with decreased vision in the R eye after falling on her face two weeks previously.
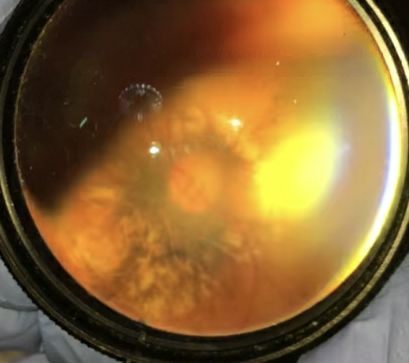
In addition to ruling out a microhyphema, corneal injury, retinal detachment and vitreous hemorrhage, you look at the fundus pictured below.
There is an abnormality of the optic nerve. What does this indicate?
A normal optic nerve for reference
Our patient had pallor of the optic nerve presumably from direct trauma since she lost vision after the fall. She also had a posterior staphyloma (which has nothing to do with staph bacteria but rather comes from the Greek for “bunch of grapes” ) and can also occur with trauma. It refers to a bulging in the wall of the globe. Staphylomas also occur without trauma in 50% of patients with pathologic myopia.
The major cause of her vision loss is traumatic optic neuropathy; direct trauma to the optic nerve. The optic nerve head appears normal initially, but optic atrophy can be seen 3-6 weeks after the event. The disc is pale as in our patient, the vision is decreased (20/400 ) with an afferent pupillary defect and there is chorioretinal atrophy surrounding the disc.
CAUSES OF OPTIC NEUROPATHY
Ischemic optic neuropathy- can be caused by inflammatory diseases of the blood vessels. Giant-cell arteritis, polyarteritis nodosa, Wegeners and RA can cause optic nerve ischemia. Blindness can also occur with changes in BP as in cardiac arrest survivors. Swelling from central retinal vein occlusion can also cause edema and ischemia of the optic nerve and retina.
Radiation induced optic neuropathy- Occurs 3months to 8 years after radiation to the brain.
Toxic optic neuropathy- can occur from ethylene glycol, ethambutol, amiodarone and pegylated interferon alpha(the treatment for Hep C)
Diseases within the optic nerve- optic neuritis occurs with multiple sclerosis and often results in decreased color vision, especially red. Often patients report pain Sarcoid can lead to optic nerve infiltration. Infections with Cryptococcus or cmv may also cause disc edema.
Compressive optic neuropathy- results from direct pressure on the optic nerve from tumor or thyroid ophthalmopathy. Often there is proptosis.
Nutritional optic neuropathy- B12 deficiency is a cause of optic atrophy.
Traumatic optic neuropathy- can occur from a gsw to the head or other trauma.
optic disc edema can result from central retiinal vein occlusion without hemorrhages.
Ohno-Matsui K, Jonas J. Posterior stapjyloma in pathologic myopia. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research 2019;70:99-109.
Levin L, et al. The treatment of traumatic optic neuropathy:the International Optic Nerve Trauma Study. Ophthalmology. 1999. 106(7):1268-77.
Kidd D, Burton B, Graham E, et al. Optic neuropathy associated with systemic sarcoidosis. 2016. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm Oct 3 (5) e 270.
Woo S, Lip G, Lip P. Associations of retinal artery occlusion and retinal vein occlusion to mortality, stroke and myocardial infarction: a systematic review Eye (Lond). 2016 Aug 30(8):1031-8.