A 31 y.o. graduate student comes in with abdominal bloating. The CT results are shown
What is the differential for new onset ascites with peritoneal studding?
Our patient had peritoneal tuberculosis. He was from India with no previous history of Tbc. Tuberculous peritonitis is increasing in prevalence. It is common in patients with immunocompromised states, chronic kidney disease, or cirrhosis of the liver It is most often caused by spread from pulmonary foci but can be caused by direct invasion of the bacillus through the bowel wall.
peritoneal thickening from adenocarcinoma
The differential for ascites with peritoneal studding includes:
METASTATIC NEOPLASMS
-Carcinomas of the GI tract and ovary( stomach,colon, appendix, gallbladder and pancreas)
-pseudomyxoma peritonei-is a more benign condition where thick gelantinous materil covers the surface of the peritoneal cavity. It is thought to be a low grade appendiceal tumor which can be debulked since the tumor does not invade abdominal organs.
- Lymphoma generally associated with herpes virus: human herpes virus 8 (also associated with Kaposi’s) and Epstein Barr virus
-sarcoma
INFECTIOUS AND INFLAMMATORY LESIONS
-granulomatous peritonitis includes tuberculosis,Histoplasmosis, or pneumocystis. It also includes sarcoid, and foreign material such as talc or barium.
-Sclerosing encapsulating peritonitis may occur in a patient on peritoneal dialysis; the cause is not known.
MISCELLANEOUS TUMORS AND TUMORLIKE LESIONS
-Endometriosis occurs in 10% of women of childbearing age
-Melanosis can be associated with cystic teratomas
- splenosis is heterotopic splenic tissue often occurring after trauma to the spleen
peritoneal pseudomyxoma
35 cases of bovine tuberculosis were reported in New York City from 2001-4 and linked to fresh cheese (queso fresco) brought to NYC from Mexico where 17% of cattle being slaughtered are positive for M. bovis. Pasteurized milk is free of the disease. Our patient had a positive omental biopsy showing tuberculosis. His ascitic fluid and pleural fluid cultures were negative. He was treated with rifampin, INH, pyrazinamide and ethambutol.
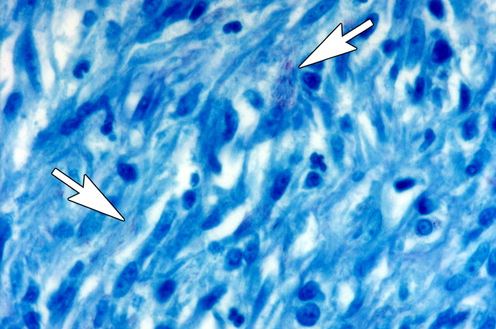
difficult to see red bacilli in the peritoneal biopsy
Levy A, Shaw J, Sobin L. Secondary tumors and tumorlike lesions of the peritoneal cavity: imaging features with pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2009. 29:347-373.
Srivastava U, Almusa O, Tung K, Heller M. Tuberculous peritonitis. Radiol Case Rep 2014;9(3):971.
MMWR Human Tuberculosis Casued by Mycobacterium bovis, New York City, 2001-2004 June 2005 54(24):605-608.